GraphQL操作可以是读操作,也可以是写操作. GraphQL查询用于在使用变异写入或发布值时读取或获取值.在任何一种情况下,操作都是一个简单的字符串,GraphQL服务器可以使用特定格式的数据解析和响应.通常用于移动和Web应用程序的流行响应格式是JSON.
定义查询的语法如下 :
//syntax 1query query_name{ someField }//syntax 2{ someField }以下是查询的示例 :
//query with name myQueryquery myQuery{ greeting}// query without any name{ greeting}从上面的例子可以清楚地看出,query关键字是可选的.
GraphQL查询有助于减少过度提取数据.与Restful API不同,GraphQL允许用户限制应从服务器获取的字段.这意味着通过网络进行较小的查询和较少的流量;这反过来缩短了响应时间.
插图1 - 使用自定义字段查询学生模型
在这个例子中,我们有一组学生存储在json文件中.每个学生模型都有firstName,lastName和id等字段,但没有fullName.在这里,我们将讨论如何进行查询以检索所有学生的fullName.为此,我们需要在两个架构解析器中创建fullName字段.
让我们看看如何使用以下步骤 : 去这个插图;
第1步和第1步;下载并安装项目所需的依赖项
创建名为 query-app 的文件夹.从终端将目录更改为 query-app .稍后,按照环境设置章节中解释的步骤3到5进行操作.
步骤2 : 号;创建模式
在项目文件夹query-app中添加 schema.graphql 文件并添加以下代码 :
type Query { greeting:String students:[Student] studentById(id:ID!):Student}type Student { id:ID! firstName:String lastName:String fullName:String }请注意,没有< students.json 文件中的i> fullName 字段.但是,我们需要通过查询获取学生的全名.在这种情况下, fullName 将是数据源无法使用的自定义字段.
步骤3 : 号;创建解析器
在项目文件夹中创建文件 resolvers.js 并添加以下代码 :
const db = require('./db')const Query = { //resolver function for greeting greeting:() => { return "hello from TutorialsPoint !!!" }, //resolver function for students returns list students:() => db.students.list(), //resolver function for studentbyId studentById:(root,args,context,info) => { //args will contain parameter passed in query return db.students.get(args.id); }}//for each single student object returned,resolver is invokedconst Student = { fullName:(root,args,context,info) => { return root.firstName+":"+root.lastName }}module.exports = {Query,Student}步骤4 : 运行应用程序
创建 server.js 文件.请参阅环境设置章节中的步骤8.在终端中执行命令 npm start.服务器将在9000端口上启动并运行.在这里,我们使用GraphiQL作为客户端来测试应用程序.
打开浏览器并输入URL http://localhost:9000/graphiql .在编辑器中输入以下查询 :
{ students{ id fullName }}查询的响应低于 :
{ "data": { "students": [ { "id": "S1001", "fullName": "Mohtashim:Mohammad" }, { "id": "S1002", "fullName": "Kannan:Sudhakaran" }, { "id": "S1003", "fullName": "Kiran:Panigrahi" } ] }}创建 server.js 并添加以下代码 :
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');const cors = require('cors');const express = require('express');const db = require('./db');const port = 9000;const app = express();//loading type definitions from schema fileconst fs = require('fs')const typeDefs = fs.readFileSync('./schema.graphql',{encoding:'utf-8'})//loading resolversconst resolvers = require('./resolvers')//binding schema and resolverconst {makeExecutableSchema} = require('graphql-tools')const schema = makeExecutableSchema({typeDefs, resolvers})//enabling cross domain calls and form postapp.use(cors(), bodyParser.json());//enabling routesconst {graphiqlExpress,graphqlExpress} = require('apollo-server-express')app.use('/graphql',graphqlExpress({schema}))app.use('/graphiql',graphiqlExpress({endpointURL:'/graphql'}))//registering portapp.listen(port, () => console.info(`Server started on port ${port}`));在终端执行命令npm start.服务器将在9000端口上启动并运行.在这里,我们使用GraphiQL作为客户端来测试应用程序.
打开浏览器并输入URL http://localhost:9000/graphiql .在编辑器中输入以下查询 :
{ students{ id fullName }}查询的响应低于 :
{ "data": { "students": [ { "id": "S1001", "fullName": "Mohtashim:Mohammad" }, { "id": "S1002", "fullName": "Kannan:Sudhakaran" }, { "id": "S1003", "fullName": "Kiran:Panigrahi" } ] }}插图2 - 嵌套查询
让我们创建一个嵌套查询来获取学生详细信息及其大学详细信息.我们将使用相同的项目文件夹.
步骤1:编辑架构
架构文件已有 student 字段.让我们添加一个田野学院并定义它的类型.
type College { id:ID! name:String location:String rating:Float}type Student { id:ID! firstName:String lastName:String fullName:String college:College}第2步和第2步;修改resolver.js
我们需要添加一个大学解析器功能,如下所示.将为返回的每个学生对象执行大学解析器功能.在这种情况下,解析器的根参数将包含 student .
const Student = { fullName:(root,args,context,info) => { return root.firstName+":"+root.lastName }, college:(root) => { return db.colleges.get(root.collegeId); }}module.exports = {Query,Student}解析器通过调用返回每个学生的大学大学收集和通过 collegeId 的获取方法.我们通过 collegeId 在学生和学院之间建立了关联关系.
第3步和第3步;测试应用程序
打开终端窗口并导航到项目文件夹.输入命令-npm start.启动浏览器并输入URL http://localhost:9000/graphiql .
在GraphiQL窗口中输入以下查询 :
{ students{ id firstName college { id name location rating } }}查询的响应如下:低于 :
{ "data": { "students": [ { "id": "S1001", "firstName": "Mohtashim", "college": { "id": "col-102", "name": "CUSAT", "location": "Kerala", "rating": 4.5 } }, { "id": "S1002", "firstName": "Kannan", "college": { "id": "col-101", "name": "AMU", "location": "Uttar Pradesh", "rating": 5 } }, { "id": "S1003", "firstName": "Kiran", "college": { "id": "col-101", "name": "AMU", "location": "Uttar Pradesh", "rating": 5 } } ] }}什么是查询变量?
如果查询有一些动态值要传递,则使用变量表示这些动态值.因此,查询可以被客户端应用程序重用.
插图
让我们创建一个简单的应用程序来理解查询变量.
第1步和第1步;编辑架构文件
添加 sayHello 字段,该字段接受字符串参数并返回字符串.客户端应用程序中的名称值将是动态的.
type Query { sayHello(name:String!):String}第2步和第2步;编辑resolver.js文件
添加 sayHello 解析器,其参数如下 :
sayHello:(root,args,context,info) => `Hi ${args.name} GraphQL server says Hello to you!!`步骤3 : 去;在GraphiQL中声明查询变量
使用$声明变量,后跟变量名称.例如:$ myname_Variable.
声明$ myname_Variable后,它必须与命名查询语法一起使用.查询,myQuery接受字符串值并将其传递给sayHello,如下所示 :
query myQuery($myname_Variable:String!) { sayHello(name:$myname_Variable)}将$ myname_Variable的值设置为"查询变量"部分中的JSON对象GraphiQL客户端.
{ "myname_Variable": "Mohtashim"}上述代码的输出如下 :
{ "data": { "sayHello": "Hi Mohtashim GraphQL server says Hello to you!!" }}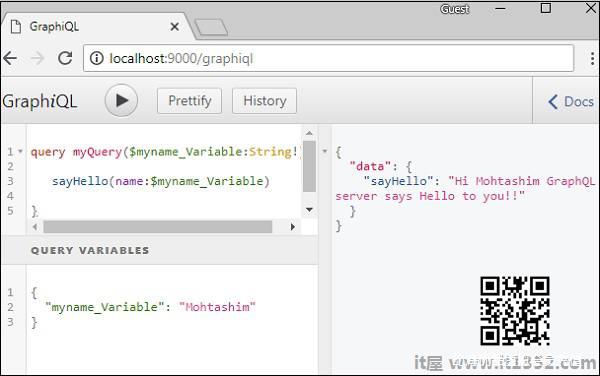
如何在枚举中使用查询变量
让我们看看当字段参数为枚举类型时如何使用查询变量./p>
第一步和第二步;编辑schema.graphql文件
enum ColorType { RED BLUE GREEN}type Query { setFavouriteColor(color:ColorType):String}setFavouriteColor 函数将enum作为输入并返回一个字符串值.
Step 2 : 编辑resolvers.js文件
解析器函数 setFavouriteColor 采用 root 和 args .在运行时传递给函数的枚举值可以通过args参数访问.
setFavouriteColor:(root,args) => { return "Your Fav Color is :"+args.color;}第3步和第3步;在GraphiQL中声明查询变量
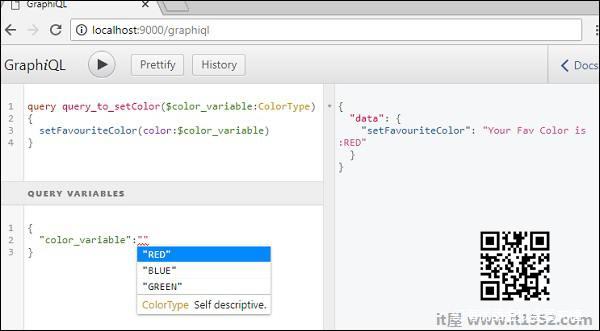
查询名为 query_to_setColor ,它采用ColorType名称color_variable的变量.此变量传递给方法setFavouriteColor.
query query_to_setColor($color_variable:ColorType) { setFavouriteColor(color:$color_variable)}在GraphiQL的查询变量部分中,输入以下代码 :
{ "color_variable":"RED"}响应显示在下面和下面;
{ "data": { "setFavouriteColor": "Your Fav Color is: RED" }}