模型在FuelPHP Web框架中起着重要作用.它代表应用程序的业务实体.它们由客户提供或从后端数据库中提取,根据业务规则进行操作并持久保存回数据库.让我们在本章中了解模型以及它们如何与后端系统交互.
创建模型
在FuelPHP中,模型简单明了PHP类扩展内置的Model类.默认情况下,模型可以使用类似于控制器的Model_作为前缀,并且应该放在 fuel/app/classes/model/文件夹中.让我们创建一个基本的员工模型,并在我们继续时扩展它.
fuel/app/classes/model/employee.php
访问模型
一旦定义了模型,它就可以在任何控制器中自由使用,只需将其包含在控制器如下.
use \Model\Employee; class Controller_Employee extends Controller { public function action_index() { $employees = Employee::fetchAll(); } }数据库概述
FuelPHP提供自己的数据库抽象层来获取来自数据库的数据.它既提供基本的,也提供基于ORM的高级工具.基本工具包由基于DB,DBUtil和Query_Builer的类组成.高级工具包是Orm. Orm工具包派生自基础工具包,并作为单独的包捆绑.
数据库配置
FuelPHP将数据库设置与主配置文件分开,该文件是 fuel/app/config/db.php .它支持每个环境的单独设置.目前,FuelPHP支持MySQL,MySQLi和PDO驱动程序.样本设置如下 :
array ( 'type' => 'mysqli', 'connection' => array ( 'hostname' => 'localhost', 'port' => '3306', 'database' => 'IT屋_fueldb', 'username' => 'root', 'password' => 'password', 'persistent' => false, 'compress' => false, ), 'identifier' => '`', 'table_prefix' => '', 'charset' => 'utf8', 'enable_cache' => true, 'profiling' => false, 'readonly' => false, ), )基于数据库的工具包
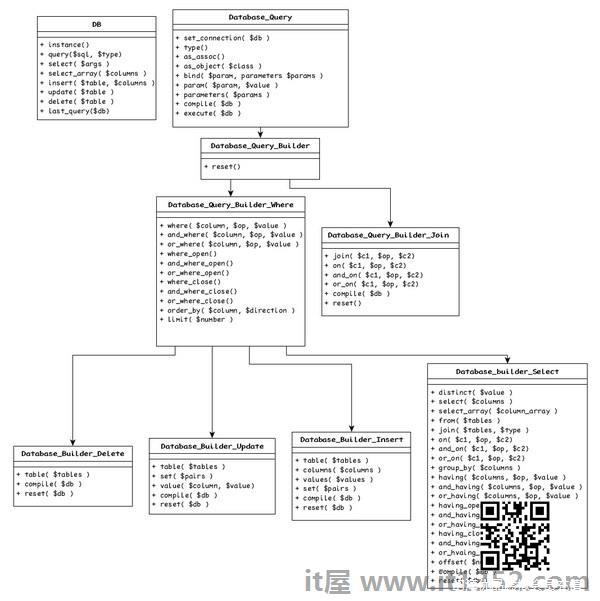
数据库类是从应用程序访问数据库的最简单选项.它提供了构建数据库查询,针对目标数据库执行它以及最终获取结果的选项. DB 类与以下类交互并提供全面的数据库API.
Database_Connection : 单例和主类与数据库交互
Database_Query : 用于执行SQL查询和获取结果的基础,具体类
Database_Query_Builder : 基础,构建SQL查询的抽象类
Database_Query_Builder_Join : 用于构建SQL连接的类
Database_Query_Builder_Where : 构建SQL查询条件的抽象类
Database_Query_Builder_Select : 用于构建SQL选择查询的具体类
Database_Query_Builder_Insert : 用于构建SQL插入查询的抽象类
Database_Query_Builder_Update : 用于构建SQL更新查询的抽象类
Database_Query_Builder_Delete : 用于构建SQL删除查询的抽象类
下图描述了类与类提供的方法之间的关系.
DB API
让我们在本节中学习DB类中最重要的方法.
instance
目的 : 创建并返回新的 Database_Connection 实例.
参数 :
$ db : 配置文件中定义的数据库连接名称,可选.
返回 : 返回 Database_Connection 对象
例如,
$db = DB::instance(); $db = DB::instance('test');查询
目的 : 准备提供的SQL语句并返回Database_Query对象,该对象可用于插入,更新,删除或从数据库中获取数据.
参数 :
$ query : SQL语句,可能包含占位符;
$ type : SQL类型,可选(DB :: SELECT,DB :: INSERT,DB :: UPDATE和DB :: DELETE)
退货 : 返回 Database_Query 对象
例如,
$query = DB::query('SELECT * FROM 'employees'');last_query
目的 : 要获取上次执行的查询
参数 : 无
返回 : 返回上次执行的查询
例如,
$employees = DB::Select('Select * from 'employee''); $sql = DB::last_query();选择
目的 : 生成查询的选择部分
参数 :
$ columns : 数据库列名列表
返回 : 返回Database_Query_Builder_Select对象
例如,
$query = DB::select(); // Select *$query = DB::select('id', 'name'); // Select id, nameselect_array(DB)
除了我们可以发送列之外,它与select类似array.
$query = DB::select_array(array('id', 'name')); // Select id, name插入
目的 : 生成查询的插入部分
参数 :
$ table_name : 数据库表的名称;
$ columns : 表列数组
返回 : 返回Database_Query_Builder_Insert对象
例如,
$query = DB::insert('employee'); // Insert into employee $query = DB::insert('employee', array('id', 'name')); // Insert into employee (id, name)更新
目的 : 生成查询的更新部分
参数 :
$ table_name : 数据库表的名称
返回 : 返回Database_Query_Builder_Update对象
例如,
$query = DB::update('employee'); // update `employee`删除
目的 : 生成查询的删除部分
参数 :
$ table_name : 数据库表的名称
返回 : 返回Database_Query_Builder_Delete对象
例如
$query = DB::delete('employee'); // delete from 'employee'查询API
Database_Query 提供了一个选项设置数据库连接,执行查询,并将结果作为关联数组或对象获取.让我们看看Database_Query类提供的方法.
set_connection
目的 : 设置要执行查询的数据库(数据库连接详细信息)
参数 : $ db - 数据库连接名称
返回 : 返回 Database_Query 对象
例如,
$query = DB::query('DELETE * FROM employee', DB::DELETE); $query->set_connection('2nd-db');param
目的 : 设置Query对象中定义的参数的值
参数 :
$ param : 参数名称;
$ value : 参数值
返回 : 返回 Database_Query 对象
例如,
// set some variables$table = 'employee';$id = 1;$name = 'Jon';// don't use$query = DB::query('SELECT * FROM '.$table.'. WHERE id = '.$id.' AND name = "'.$name.'"');// but use$query = DB::query('SELECT * FROM :tablename WHERE id = :id AND name = :name');$query->param('tablename', 'employee');$query->param('id', $id);$query->param('name', $name);类似方法
参数是一个类似的对象,除了它提供了多个选项值一次.
$query->parameters (array( 'tablename' => $table, 'id' => $id, 'name' => $name });
bind
目的 : 将变量设置为Query对象中定义的参数
参数 :
$ param : 参数名称
$ var : 用于将参数绑定到
返回 : 返回 Database_Query 对象
例如,
// bind a query parameter $table = 'employee'; $query = DB::query('DELETE * FROM :tablename', DB::DELETE); $query->bind('tablename', $table); // update the variable $table = 'employee_salary'; // DELETE * FROM `employee_salary`; $sql = $query->compile();编译
目的 : 编译定义到SQL查询中的查询对象
参数 :
$ db : 连接字符串,可选
返回 :
例如,
// assign a value to a query parameter $table = 'employee'; $query = DB::query('DELETE * FROM :tablename', DB::DELETE); $query->param('tablename', $table);// compile the query, returns: DELETE * FROM employee $sql = $query->compile();执行
目的 : 执行Query对象中定义的查询并返回结果
参数 :
$ db : 数据库连接名称
返回 : 返回结果
例如,
// assign a value to a query parameter $table = 'employee'; $query = DB::query('DELETE * FROM :tablename', DB::DELETE); $query->param('tablename', $table); // execute the query $query->execute();as_assoc
目的 : 将返回类型设置为关联数组而不是对象
参数 : 无
返回 : 返回当前对象
例如,
$query = DB::query('SELECT * FROM employee', DB::SELECT); $result = $query->as_assoc()->execute(); foreach ($result as $row) { echo $row['id']; }as_object
目的 : 将返回类型设置为对象而不是关联数组
参数 : 无
返回 : 返回当前对象
例如,
$query = DB::query('SELECT * FROM employee', DB::SELECT); $result = $query->as_object()->execute(); foreach ($result as $row) { echo $row->id; } // have ORM model objects return instead $result = $query->as_object('Model_Employee')->execute();Query Builder API
查询构建器(Query_Builder)基于类提供构建选项SQL动态查询.它有四个类,每个类选择(Query_Builder_Select),插入(Query_Builder_Insert),更新(Query_Builder_Update)并删除(Query_Builder_Delete )查询.这些类派生自 Query_Builder_Where 类(生成条件的选项),它本身派生自 Query_Builder ,所有类的基础.
让我们看一下Query_Builder类提供的方法.
选择
目的 : 生成选择查询的列.
参数 :
$ columns : 列列表,可选
返回 : 返回当前实例
例如,
$ query = DB :: select('name')//select`name` $ query = DB :: select(array('first_name','name'))//选择`first_name`为`姓名`来自
目的 : 要生成选择查询的表格详细信息
参数 :
$ tables : 表格列表
退货 : 返回当前实例
例如,
$ query = DB :: select('name') - > from('employee')//从`employee`中选择`name`其中
目的 : 生成选择,插入和更新查询的条件
参数 :
$ column : 列名或数组($ column,$ alias);
$ op : 逻辑运算符,=,!=,IN,BETWEEN和LIKE,可选;
$ value : 列值
返回 : 返回当前实例
例如,
$ query = DB :: select('name') - > from('employee') $ query = $ query-> where('name','=','Jon'); //从`employee`中选择`name`,其中`name` =`Jon`;类似方法
类似的方法是where_open(),and_where_open(),or_where_open(),where_close() ,and_where_close(),or_where_close().它们类似于where()方法,除了它们在条件周围添加额外的关键字和括号.以下是示例代码.
$query = DB::select('*')->from('employee'); $query->where('email', 'like', '%@gmail.com'); $query->or_where_open(); $query->where('name', 'Jon'); $query->and_where('surname', 'Peter');$query->or_where_close(); // SELECT * FROM `employee` WHERE `email` LIKE "%gmail.com" OR (`name` = "Jon" AND `surname` = "Peter")加入
目的 : 生成选择查询的表联接
参数 :
$ table : 表名或数组($ table,$ alias);
$ type : 加入类型(左,右,内等)
退货 : 返回当前实例
示例
$ query = DB :: select('name') - > from('employee') - > join('employee_salary')//从`employee`中选择`name`加入`employee_salary`目的 : 去;要在选择查询中生成联接条件
参数 :
$ c1 : 数组中包含别名的表名或表名;
$ op : 逻辑运算符;
$ c2 : 表名或表名,数组中包含别名
返回 : 返回当前实例
例如,
$ query = DB :: select('name') - > from('employee') - > join('employee_salary') $ query = $ query-> on('employee.employee_id' ,'=','employee_salary.employee_id')//从'employee`中选择`name`在//`employee.employee_id` =`employee_salary.employee_id` $ b $上的`employee_salary` b类似方法
相关方法是and_on()和or_on().它们类似于on(),除了它们在连接周围添加额外的关键字和括号.
group_by
目的 : 按查询生成分组
参数 : $ columns : 用于对结果进行分组的列名
返回 : 返回当前实例
例如,
$query = DB::select('name')->from('employee') $query = $query->group_by('name'); // select `name` from `employee` group by `name`目的 : 按SQL查询条件生成组
参数 : $ column : 列名或数组($ column,$ alias); $ op : 逻辑运算符,=,!=,IN,BETWEEN和LIKE,可选; $ value : 列值
返回 : 返回当前实例
示例
$query = DB::select('name')->from('employee')$query = $query->group_by('name');$query = $query->having('name', '!=', 'Jon');// select `name` from `employee` group by `name` having `name` != `Jon`类似方法
类似的方法有having_open(),and_having_open(),or_having_open(),having_close(),and_having_close(),or_having_close().它们类似于having()方法,除了它们在条件周围添加额外的关键字和括号.
重置
目的 : 要重置查询
参数 : 无
返回 : 返回当前实例
例如,
$query = DB::select('name')->from('employee') $query->reset() $query = DB::select('name')->from('employee_salary') // select `name` from `employee_salary`DBUtil class
DBUtil类提供管理和执行例行数据库操作的选项.一些重要的方法如下 :
set_connection - 设置默认连接
DBUtil :: set_connection('new_database');create_database - 创建数据库.
DBUtil :: create_database('my_database');drop_database - 删除数据库.
DBUtil :: drop_database('my_database');table_exists - 检查给定的表是否存在.
if(DBUtil::table_exists('my_table')) { // Table exists } else { // Table does NOT exist, create it! }drop_table - 删除表格.
DBUtil :: drop_table('my_table');create_table - 创建一个表.
\DBUtil::create_table ( 'users', array ( 'id' => array('type' => 'int', 'auto_increment' => true), 'name' => array('type' => 'text'), ), );Orm Toolkit
FuelPHP使用基于流行的活动记录模式
'always_load' => array ( 'packages' => array ( 'orm', ), ),
创建模型
Orm提供基本模型类Orm \ Model.我们需要使用orm模型扩展我们的模型以使用ORM功能.以下是示例代码.
class Model_Employee extends Orm\Model {}配置
Orm提供了一组设置,用于配置模型以使用ORM功能.它们如下 :
连接 : 在模型中设置静态 _connection 属性以指定连接名称.
class Model_Employee extends Orm\Model { protected static $_connection = "production"; }表名 : 在模型中设置静态 _table_name 属性以指定后端表的表名.
class Model_Employee extends Orm\Model { protected static $_table_name = 'employee'; }主键 : 在模型中设置静态 _primary_key 属性以指定后端表的主键.
class Model_Employee extends Orm\Model { protected static $_primary_key = array('id'); }列 : 在模型中设置静态_properties属性以指定后端表的列.它支持data_type,label,validation,form elememts等.
class Model_Employee extends Orm\Model { protected static $_properties = array ( 'id', 'name' => array ( 'data_type' => 'varchar', 'label' => 'Employee Name', 'validation' => array ( 'required', 'min_length' => array(3), 'max_length' > array(80) ), 'form' => array ( 'type' => 'text' ), ), 'age' => array ( 'data_type' => 'int', 'label' => 'Employee Age', 'validation' => array ( 'required', ), 'form' => array ( 'type' => 'text' ), ), ); }条件 : 设置静态 _conditions 属性以按选项设置条件和顺序.
class Model_Employee extends Orm\Model { protected static $_conditions = array ( 'order_by' => array('id' => 'desc'), 'where' => array ( array('is_active', > true), ), ); }观察员 : Orm 提供基于观察者的事件系统,以向特定事件添加行为.要添加行为,请首先在模型中设置 _observers 属性.然后,将行为定义为类,并将其与事件一起设置在 _observers 属性中.如果未指定任何事件,则将为所有事件调用该行为.我们也可以指定多个行为.
class Model_Employee { protected static $_observers = array ( 'example', // will call Observer_Example class for all events 'Orm\\Observer_CreatedOn' => array ( 'events' => array('before_insert'), // will only call Orm\Observer_CreatedOn at before_insert event ) ); }创建
配置模型后,我们可以立即开始使用这些方法. Orm 提供 save 方法将对象保存到数据库中.我们可以使用已配置的属性设置数据,如下所示 :
// option 1 $new = new Model_Employee(); $new->name = 'Jon'; $new->save(); // option 2, use forge instead of new $new = Model_Employee::forge();$new->name = 'Jon'; $new->save(); // option 3, use array for properties $props = array('name' => 'Jon'); $new = Model_Employee::forge($props); $new>save();读取
Orm提供了一种方法,可以从数据库中获取数据并绑定到对象中. find方法根据输入参数工作.让我们看看不同的选项 :
按主键 : 指定主键通过匹配已配置表的主键来返回记录.
$ employee = Model_Employee :: find(1);
第一个/最后一个记录 : 指定'first'或'last'将分别获取第一条记录或最后一条记录.我们也可以通过选项传递订单.
$ entry = Model_Employee :: find('first'); $ entry = Model_Article :: find('last',array('order_by'=>'id'));全部 : 指定"all"将从配置的表中获取所有记录.我们可以通过选项和条件指定订单.
$entry = Model_Employee::find('all'); $entry = Model_Article::find ('all', array ( 'where' => array ( array ('name', 'Jon'), ), 'order_by' => array ('id' => 'desc'), ));我们可以使用基本数据库工具包的查询API以及高级搜索选项的模型,如下所示.
$ query = Model_Employee :: query() - > where('category_id',1) - > order_by('date','desc'); $ number_of_employees = $ query-> count(); $ latest_employee = $ query-> max('id'); $ young_employee = $ query-> min('age'); $ newest_employee = $ query-> get_one(); $ employees = $ query-> limit(15) - > get();更新
更新模型与创建相同,只是不是创建新模型而只是获取模型要使用find方法更新,请更新属性,然后按如下方式调用save方法.
$ entry = Model_Employee:find(4) ; $ entry-> name ='Peter'; $ entry-> save();
删除
Orm提供了删除模型的删除方法.只需获取对象并调用delete方法.
$ entry = Model_Employee:find(4); $ entry-> delete();
Working Example
Let’s create a working example in this chapter to understand the model and database.
Create a Database
Create a new database in MySQL server, using the following command.
create database it1352_fueldb
Then, create a table inside the database using the following command.
create table employee(id int primary key, name varchar(20), age int not null);
Configure the Database
Let us configure the database using database configuration file, *fuel/app/config/db.php. Add the following changes to connect MySQL server.
array ( 'type' => 'mysqli', 'connection' => array ( 'hostname' => 'localhost', 'port' => '3306', 'database' => 'IT屋_fueldb', 'username' => 'root', 'password' => 'pass', 'persistent' => false, 'compress' => false, ), 'identifier' => '`', 'table_prefix' => '', 'charset' => 'utf8', 'enable_cache' => true, 'profiling' => false, 'readonly' => false, ), 'production' => array ( 'type' => 'mysqli', 'connection' => array ( 'hostname' => 'localhost', 'port' => '3306', 'database' => 'IT屋_fueldb', 'username' => 'root', 'password' => 'pass', 'persistent' => false, 'compress' => false, ), 'identifier' => '`', 'table_prefix' => '', 'charset' => 'utf8', 'enable_cache' => true, 'profiling' => false, 'readonly' => false, ), );
Include ORM Package
Update the main configuration file, fuel/app/config/config.php to include ORM package by adding the following configuration.
'always_load' => array ( 'packages' => array ( 'orm' ), ),
Now, ORM is enabled in your application
Create Employee Model
Create a new model, Employee under the model folder "fuel/app/classes/model". It is defined as follows.
Employee.php
array ( 'data_type' => 'varchar', 'label' => 'Employee Name', 'form' => array ( 'type' => 'text' ), ), 'age' => array ( 'data_type' => 'int', 'label' => 'Employee Age', 'form' => array ( 'type' => 'text' ), ), ); }
Create Action
Create new action, action_model in Employee controller located at fuel/app/classes/controller/employee.php as follows.
class Controller_Employee extends Controller { public function action_model() { // db based sql command to delete all employees $query = db::query('delete from `employee`'); $query->execute('production'); // orm based query to add new employees $model = new model_employee(); $model->name = "john"; $model->age = 25; $model->save(); $model = new model_employee(); $model->name = "peter"; $model->age = 20; $model->save(); // orm based query to fetch all employee data $data = array(); $data['emps'] = model_employee::find('all'); return response::forge(view::forge('employee/model', $data)); } }Create View
Now, create a view file model.php located at "fuel/app/views/employee". Add the following changes in the file.
Now, request the URL, http://localhost:8080/employee/model and it will produce the following result.