二进制搜索树(BST)是一个树,其中所有节点都遵循下面提到的属性 :
节点的左子树有一个小于或等于其父节点密钥的密钥.
节点的右子树有一个大于其父节点键的键.
因此,BST将其所有子树划分为两个段;左子树和右子树可以定义为 :
left_subtree (keys) ≤ node (key) ≤ right_subtree (keys)
表示
BST是以维护BST属性的方式排列的节点集合.每个节点都有一个密钥和一个相关的值.在搜索时,将所需的键与BST中的键进行比较,如果找到,则检索相关值.
以下是BST的图示表示 :
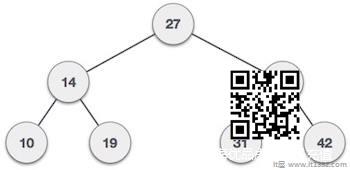
我们观察到根节点密钥(27)具有所有值较小的密钥左侧子树和右侧子树上的高值键.
基本操作
以下是树的基本操作 :
搜索 : 搜索树中的元素.
插入 : 在树中插入元素.
预订遍历 : 以预购方式遍历树.
按顺序遍历 : 按顺序遍历树.
订购后遍历 : 以后序方式遍历树.
节点
定义一个有一些节点的节点数据,对其左右子节点的引用.
struct node { int data; struct node *leftChild; struct node *rightChild;};搜索操作
每当要搜索元素时,从根节点开始搜索.然后,如果数据小于键值,则搜索左子树中的元素.否则,搜索右子树中的元素.对每个节点遵循相同的算法.
算法
struct node* search(int data){ struct node *current = root; printf("Visiting elements: "); while(current->data != data){ if(current != NULL) { printf("%d ",current->data); //go to left tree if(current->data > data){ current = current->leftChild; } //else go to right tree else { current = current->rightChild; } //not found if(current == NULL){ return NULL; } } } return current;}插入操作
每当要插入元素时,首先找到其正确的位置.从根节点开始搜索,然后如果数据小于键值,则在左子树中搜索空位置并插入数据.否则,搜索右子树中的空位置并插入数据.
算法
void insert(int data) { struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node)); struct node *current; struct node *parent; tempNode->data = data; tempNode->leftChild = NULL; tempNode->rightChild = NULL; //if tree is empty if(root == NULL) { root = tempNode; } else { current = root; parent = NULL; while(1) { parent = current; //go to left of the tree if(data < parent->data) { current = current->leftChild; //insert to the left if(current == NULL) { parent->leftChild = tempNode; return; } } //go to right of the tree else { current = current->rightChild; //insert to the right if(current == NULL) { parent->rightChild = tempNode; return; } } } }}