在来自独立来源的随机数据集中,通常观察到数据的分布是正常的.这意味着,在绘制一个图表时,水平轴上的变量值和垂直轴上的值的计数,我们得到一个钟形曲线.曲线的中心表示数据集的平均值.在图中,百分之五十的值位于均值的左侧,另外百分之五十位于图的右侧.这在统计学中称为正态分布.
R有四个内置函数来生成正态分布.它们如下所述.
dnorm(x,mean,sd) pnorm(x,mean,sd) qnorm(p,mean,sd) rnorm(n,mean,sd)
以下是上述函数中使用的参数的说明 : ;
x 是一个数字向量.
p 是一个概率向量.
n 是观察次数(样本量).
均值是样本数据的平均值.它的默认值为零.
sd 是标准偏差.它的默认值是1.
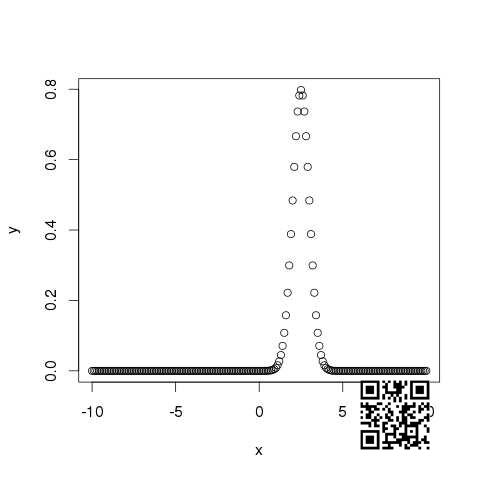
dnorm()
此函数给出概率的高度给定均值和标准差的每个点的分布.
# Create a sequence of numbers between -10 and 10 incrementing by 0.1.x <- seq(-10, 10, by = .1)# Choose the mean as 2.5 and standard deviation as 0.5.y <- dnorm(x, mean = 2.5, sd = 0.5)# Give the chart file a name.png(file = "dnorm.png")plot(x,y)# Save the file.dev.off()
当我们执行上面的代码时,它产生以下结果 :
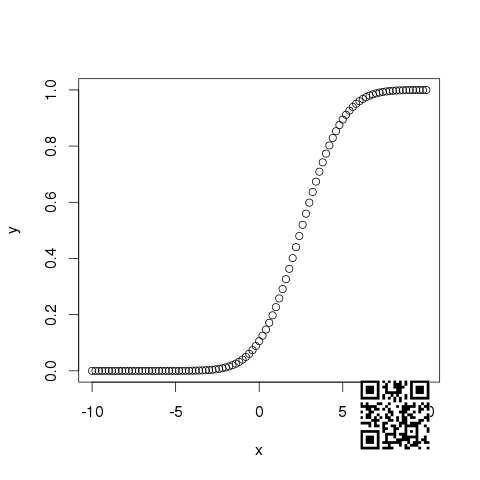
pnorm()
此函数给出正态分布的随机数的概率小于给定数的值.它也被称为"累积分布函数".
# Create a sequence of numbers between -10 and 10 incrementing by 0.2.x <- seq(-10,10,by = .2) # Choose the mean as 2.5 and standard deviation as 2. y <- pnorm(x, mean = 2.5, sd = 2)# Give the chart file a name.png(file = "pnorm.png")# Plot the graph.plot(x,y)# Save the file.dev.off()
当我们执行上面的代码时,它产生以下结果 :
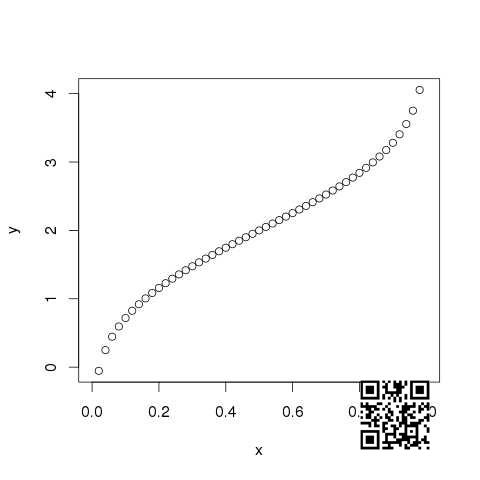
qnorm()
此函数需要概率值并给出一个累积值与概率值匹配的数字.
# Create a sequence of probability values incrementing by 0.02.x <- seq(0, 1, by = 0.02)# Choose the mean as 2 and standard deviation as 3.y <- qnorm(x, mean = 2, sd = 1)# Give the chart file a name.png(file = "qnorm.png")# Plot the graph.plot(x,y)# Save the file.dev.off()
当我们执行上面的代码时,它产生以下结果 :
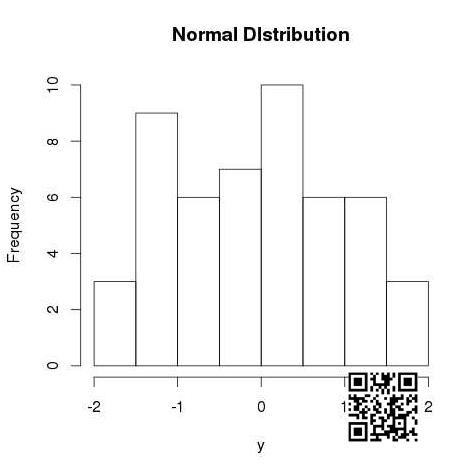
rnorm()
此函数是用于生成分布正常的随机数.它将样本大小作为输入并生成许多随机数.我们绘制直方图以显示生成数字的分布.
# Create a sample of 50 numbers which are normally distributed.y <- rnorm(50)# Give the chart file a name.png(file = "rnorm.png")# Plot the histogram for this sample.hist(y, main = "Normal DIstribution")# Save the file.dev.off()
当我们执行上面的代码时,它产生以下结果 :